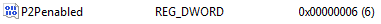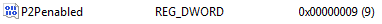Content Distribution Cache
The product formerly referred to as Nomad has been rebranded as Content Distribution. Although the new name is implemented in the majority of documentation and user interfaces, references to Nomad may still appear in specific tools, scripts, or contexts.
An overview of the Content Distribution cache including different methods used by Content Distribution peers to access the cache on the elected master. The Content Distribution cache is essential to the Download once to branch feature. The cache enables Content Distribution to hold its downloaded content so that it can be distributed locally to other peers. The cache contains downloaded content (such as packages, applications, and software updates) which can vary in size from relative small patches to rather large OS image files.
Content Distribution cache is used in a number of deployment scenarios. For example scenarios and how you can monitor those deployments using the Content Distribution app refer to:
Hard links
Content Distribution uses file system hard links between the Content Distribution and Configuration Manager client caches, ensuring that only a single copy of the content is retained. The use of hard links can be disabled using the NoHardlink setting.
Hard links are used for all content types except:
-
Office 365 Updates, as this type of content is retained in the Office 365 Click To Run agent installation folder rather than the CCM cache folder.
-
Content downloaded from Cloud Distribution Points.
A hard link is the file system representation of a file by which more than one path references a single file in the same volume. Content Distribution uses this technique when making files in its cache available to the Configuration Manager cache if both of them are on the same volume and hard linking is not disabled. Both caches will hold the files but only uses one footprint on the physical volume. The Content Distribution cache is defined in the LocalCachePath registry value which is set during installation using the MODULE.NOMAD.CACHEPATH installer property. If these caches are on different volumes, or hard linking is disabled, then Content Distribution copies content to the Configuration Manager cache.
Irrespective of whether hard linking is used or not, the following applies:
-
The Configuration Manager client and Nomad Branch each independently manages the content in their respective cache folders.
-
When Content Distribution removes content from its cache as part of cache management, it also removes the same content from the Configuration Manager cache. Refer to Cache management.
-
When Configuration Manager removes content from its cache, content in the Content Distribution cache is not purged.
-
Content downloaded directly by the Configuration Manager client (outside of Content Distribution) is not hard linked or copied to the cache.
-
If the Configuration Manager client does not have sufficient space in its cache, it will not request a Content Distribution download.
Peer access methods
Content Distribution uses peer-to-peer connections to enable its peers to access the Content Distribution master's cache. Content Distribution can share content with peers either through a file share (using Windows File and Printer Sharing Services) over SMB, or through an HTTP web service implemented in the Content Distribution client. Content Distribution also supports a 'connectionless' option for sharing content over UDP, but this should only be used as a last resort if SMB or HTTP/S are not viable in your environment.
Due to the complexity of network environments, Content Distribution provides some low-level control over the way the P2P communications are handled to help overcome certain scenarios that may arise. Specifically Content Distribution has a number of peer-to-peer connection related enhancements that enable it to work where:
-
File and Print Sharing Services are disabled.
-
The connections may switch between wired and wireless communications.
-
A multi-forest environment where peer computers from different forests may co-exist in the same subnet and are unable to access the Content Distribution master share using its hostname alone.
-
Large files are being transferred.
HTTP/S
Content Distribution can be configured to use HTTP or HTTPS for all P2P sharing – thereby eliminating its dependency on SMB and File and Printer Sharing Services. Content Distribution also supports certificate-based client authentication, which eliminates the local SMSNomadP2P& account previously required for clients to authenticate with the elected master. For more detail please refer to Peer copy over HTTP or HTTPS.
This is the recommended method of peer sharing content.
SMB and File and Printer Sharing Services
This is the original and default method for Content Distribution peer sharing, which uses SMB and requires File and Printer Sharing Services. Refer to The Content Distribution share.
Connectionless P2P
Content Distribution can be configured to bypass these services and use the connectionless transfer protocol over the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) instead. Connectionless P2P does not use authentication and is approximately five times slower than SMB. This transfer method is only recommended for environments where other methods are not available.
To enable Connectionless P2P update the P2PEnabled registry value on all Content Distribution clients to:
-
0x0000: P2P disabled.
-
0x0002: Enable connectionless P2P server.
-
0x0004: Enable connectionless P2P client.
In most cases both P2P server and P2P client should be enabled, by setting 0x0006 (decimal 6), as shown.
The Content Distribution share
The Content Distribution cache is configured as a share that enables peer-to-peer distribution of downloaded content. Content Distribution provides control over the accounts that have access to the share and also provides an advanced Content Distribution FanOut mechanism that can overcome the connection limit to shares on workstations to ensure that content is distributed efficiently and securely.
If Content Distribution is configured to use exclusively HTTP/HTTPS for peer copy, then the share is not created by the NomadBranch service.
Enhanced Content Distribution share security
Content Distribution leverages native Windows security to define which accounts have access to the share. In Content Distribution’s default configuration, a share is created when the Content Distribution service is started and removed when it is stopped. The default Content Distribution settings also grants both Authenticated Users and the SMSNomadP2P& share account read-only access to the share.
In early versions of Content Distribution, further restricted access to the share could only be done using custom share permissions. The major disadvantage to this approach was that the Content Distribution service no longer managed the share, and it had to be created and managed through other methods. So, if you wanted to exclude Authenticated Users from the share permissions, you must take over the management of the share.
In Content Distribution, a cache access security option has been implemented that is controlled using the AuthenticatedUsers registry value. This optionally restricts access to the share to just the SMSNomadP2P& share account, thereby excluding Authenticated Users from the share permissions but still leaves Content Distribution in control of the creation, management and removal of its share.
Nomad Branch service and the share
The share is created each time the Nomad Branch service starts and removed when it stops.
When the Nomad Branch service starts:
-
A share called NomadSHR for the Content Distribution cache folder is created. The share is removed when the Nomad Branch service stops. If this share is created on a workstation, only 6 concurrent users can access it. If the share is created on a server, there is no limitation.
-
A local user account called SMSNomadP2P& is created with its password attribute set to Password Never Expires. This account is not removed when the Nomad Branch service stops. The password for this account is changed each time the Content Distribution service restarts and is made up of 14 characters using a combination of upper and lower case alpha-numeric characters. This account is not a domain user and does not have the logon locally privilege. Account details are requested by peer clients during the Election rules and master elections process.
-
If the AuthenticatedUsers registry value is configured to use the built-in security principal Authenticated Users, the NTFS permissions on the cache folder are updated so that Authenticated Users is granted Read and Execute, List folder contents and Read permissions for the folder, its subfolder and files. These NTFS permissions are not removed when the Nomad Branch service stops.
Share Permissions for NomadSHR is configured as Read-only for the local SMSNomadP2P& user account and optionally a built-in security principal as specified by the AuthenticatedUsers registry value. The default is:
-
Local user account SMSNomadP2P&
-
Built-in security principal Authenticated Users
The default location for the Content Distribution cache is C:\ProgramData\1E\NomadBranch. The MODULE.NOMAD.CACHEPATH installer property is also used to configure the location of the cache, which is stored in the registry value LocalCachePath.
You can use the MODULE.NOMAD.SPECIALNETSHARE installer property or update the SpecialNetShare registry value so that Content Distribution hides the share. If you do this, the share will be renamed NomadSHR$ and you will need to update all Content Distribution installations to use the hidden share.
Content Distribution can also be configured to use the machine account for peer connections instead of the local SMSNomadP2P& account by using the MODULE.NOMAD.SPECIALNETSHARE installer property or by updating the SpecialNetShare registry value. If the machine account is used, the local SMSNomadP2P& account is not created. Machine$ accounts in trusted domains are considered as Authenticated Users. The AuthenticatedUsers registry value must include Authenticated Users. Peer clients must be in trusted domains.
Use the MODULE.NOMAD.AUTHENTICATEDUSERS installer property or update the AuthenticatedUsers registry value to configure read-only access to the share for Authenticated Users (default), Everyone or neither in addition to the Content Distribution Share Account SMSNomadP2P&. If Authenticated Users is selected, additional NTFS permissions are also configured for Authenticated Users on the Content Distribution cache folder.
The difference between Authenticated Users and Everyone depends on the OS version but in general Everyone includes Authenticated Users plus Guest.
Domain controllers
When Content Distribution is installed on a domain controller (DC), it does not create the SMSNomadP2P& account and does not create the share. This is because it is not possible to create a local account on a DC. Content Distribution will not respond to elections and cannot be elected as a master.
-
If software is targeted at a DC, Content Distribution downloads the content from the distribution point (DP).
-
If the DC is also a DP, Content Distribution continues to process LsZ files and respond to Content Distribution clients as normal.
Custom share permissions
The SpecialNetShare registry values enables administrators to create their own share called NomadSHR, set the user limit and permissions. The cache is shared as NomadSHR, giving read access to the local Content Distribution share account and authenticated users. This enables new peer connections to be established and also allows access to the cache for computers with existing connections.
Share permissions can be configured on the share and requires the minimum read-only permission for:
-
The local user account SMSNomadP2P& if not using the machine account.
-
Built-in security principal Authenticated Users if using the machine account.
NTFS security can also be set on the Content Distribution cache folder and requires these minimum permissions:
-
Built-in security principal SYSTEM requires Full control permission (because the Nomad Branch service uses the local system account).
-
Local group Users requires Read & execute, List folder contents, and Read permissions.
-
Local group Administrators requires Full control permission.
In addition, if using the built-in security principal Authenticated Users, as required when using the machine account, it requires NTFS security permissions Read & execute, List folder contents and Read.
Switching between wireless and wired network connections
When network connections are switched between wireless and wired, Content Distribution may encounter problems accessing the share. Problems are likely to occur if DHCP uses a short lease time and the DNS does not reflect these changes quick enough. To mitigate these issues, Content Distribution has support for net literal names (IP addresses) for identifying its shares. Content Distribution clients normally use the elected master's hostname to connect to the NomadSHR in order to download the LSZ, LST and package files.
To configure Content Distribution to use net literal names (IP addresses) when connecting to peer shares, update the P2PEnabled registry value to include the following:
-
0x0001: P2P enabled.
-
0x0008: Enable use of net literal names (IP addresses).
For example, P2P enabled 0x1 plus enable use of net literal names 0x8, by setting 0x0009 (decimal 9), as shown below.
Multi-forest environments
By default, Content Distribution clients use the master's hostname to connect to the master in order to retrieve the package and signature files.
In a multi-forest environment computers from different forests may be present in the same subnet as the peers and are not able to connect to the master using just the hostname. In this scenario, Content Distribution should be configured to use FQDN for peer-to-peer connections. For this to work, it is necessary that the reverse lookup for IP addresses is correctly configured and running. If this is not available, Content Distribution reverts to using the IP address for its connection to P2P shares.
To configure Content Distribution to use FQDN when connecting to peer shares, update the P2PEnabled registry value to include:
-
0x0001: P2P enabled.
-
0x0010: Enable use of FQDN name.
For example P2P enabled 0x1 plus enable use of FQDN 0x10, by setting 0x0011 (decimal 17), as shown.