How NightWatchman Enterprise works
NightWatchman power management reduces energy costs by automatically powering down computers across your network overnight and at weekends. This helps you to significantly reduce energy consumption without impacting user productivity and all from a central location.
The combination of NightWatchman and WakeUp provides a scalable proven solution for power and patch management. They revolutionize the ability of any organization to safely and remotely power manage its computers, ensuring they are all on, available when needed, and saving power at other times.
Power and patch management rapidly delivers significant cost savings and reductions in energy and carbon emissions while ensuring users continue to work productively.
NightWatchman power management features
The main points of NightWatchman Enterprise's power management features.
|
Feature |
Explanation |
|---|---|
|
Scheduled power events |
You can set specific times to trigger a power event (safe power down, hibernate or sleep) placing computers in a low power state. |
|
Safe power down |
If a group of computers must be powered down (or rebooted as part of a patching process for example), dealing with open documents is a challenge. NightWatchman comes with an extensible document automation feature allowing users’ work to be saved prior to system shutdown. |
|
Sleepless client detection |
Certain application interactions with the operating system have the unnecessary side effect of keeping computers from going into a sleep state. NightWatchman can detect the processes that keep a computer awake and enables you to override them, enabling additional power savings to be achieved. |
|
Alarm clock |
You can set a time when NightWatchman will bring a computer out of a sleep state. |
|
Maintenance windows |
You can define maintenance windows where computers are brought out of a low power state for maintenance to be carried out and return them back to that low power state after. This enables antivirus scans, patch management and indexing to occur out-of-band, whilst still achieving maximum power savings. |
|
Keep active |
Users can opt-out of power management for a period of time so that they have control to run a large download environment. |
|
Administrative flexibility |
You can use VBScripts to extend NightWatchman to meet unique scenarios or unusual requirements that are specific to your environment. |
How WakeUp works
WakeUp provides the ability to power-on computers from a powered-off state over a network, it integrates with either the NightWatchman Management Centre or Configuration Manager. Integrating with NightWatchman Management Centre gives you wake up functionality as well as defining power policies with alarm clocks and maintenance windows which makes use of WakeUp to cover computers that are powered-off. Integrating with Configuration Manager ensures computers are powered-up or down where necessary or push software updates regardless of whether computers are on or are in the process of being woken up. WakeUp ensures computers check for any deployments that are due immediately, thereby circumventing the normal polling cycle – it is an invaluable tool for critical emergency patch management.
Organizations have typical management tasks such as software installation, upgrades and hot-fixes, data backup, system inventory and critical patch management that generally need to be performed across their network. Performing these tasks during the day can have a negative impact on user productivity and network resources – particularly for critical patches that require reboots.
To avoid interrupting users, organizations often prefer to run such tasks outside business hours. This is made easier using remote management software. Traditionally this requires asking users to leave their computers switched on overnight. It may also be necessary to have technicians work during off-hours to physically visit each computer to turn it on.
WakeUp allows administrators to remotely and securely power-on computers to deploy patches and upgrades out-of-hours, minimizing user disruption. By ensuring computers are always patched and up-to-date, WakeUp reduces helpdesk support calls and improves user productivity. It integrates remote wakeup (Wake-on-LAN) technology with either Configuration Manager or the NightWatchman Management Centre to ensure that computers are fully powered-on whenever they are needed.
WakeUp has the following features:
|
WakeUp Feature |
Explanation |
|---|---|
|
Dynamic proxy agent |
Uses a highly secure, dynamic proxy agent based Wake-on-LAN solution eliminating the need for subnet directed broadcast or other changes to network infrastructure. |
|
Highly scalable |
Stagger the software distribution per site dramatically reducing the load on the site servers and increasing both patch success and efficiency. |
|
Last Man Standing |
Implements a unique technology where at least one machine on a subnet is guaranteed to be available to wake its peers. |
|
On-demand WakeUp |
Provides wake up from power-off capabilities to the NightWatchman Management Center console. This allows individual computers to be woken directly from the console. |
|
Extensive reporting |
Provides reports on the success of Wake-on-LAN activities. |
Additionally, in Configuration Manager environments, you benefit from:
|
Configuration Manager benefit |
Explanation |
|---|---|
|
Configuration Manager integrated Wake-on-LAN |
WakeUp continually monitors the Configuration Manager database to automatically wake computers that are targeted for new software distributions, patches or OS upgrades prior to the deployment start time. |
|
On-demand WakeUp |
You can manually wake up individual computers or entire collections from a low power state from a right-click context-menu. |
|
Configuration Manager acceleration-policy refresh and hardware inventory refresh |
Supports pro-active policy refresh and updates the hardware inventory when it detects a change on a subnet. This enables Configuration Manager infrastructure to react quicker and be more up-to-date in a way that does not impact its efficiency and scalability. |
|
Extensive network wake state reporting |
Provides reports on the success rates of Configuration Manager deployments involving a wake up as well as information on failures and the reason for it. |
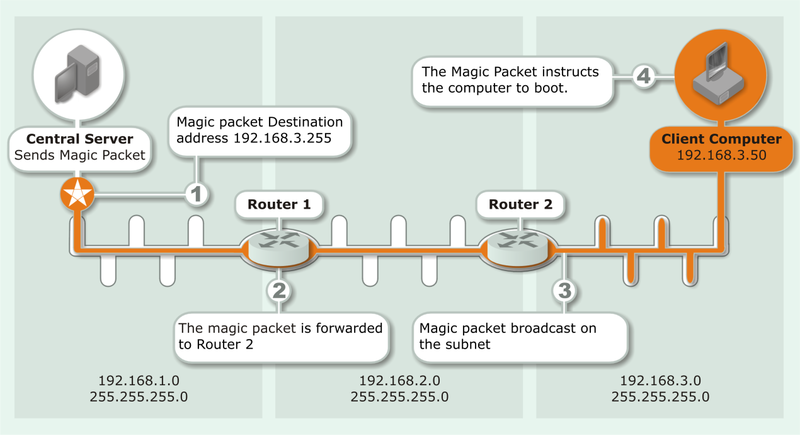
WakeUp uses Wake-on-LAN technology in combination with NightWatchman Management Center or Configuration Manager to wake up configured computers. It is a technology which allows administrators to remotely power on systems from sleep or standby mode and must be supported by both the operating system and the system hardware. A Wake-on-LAN aware network adapter is able to draw power from a special power supply that delivers a certain amount of power continually, even when the system is switched off. The network adapter continuously monitors the network, watching for a magic packet.
A magic packet is a special network packet which contains repeated MAC address information. The network card listens out for a magic packet destined for its MAC address. When the packet is received, the network adapter sends a message to the motherboard to initiate boot up.
What are subnet directed broadcasts?
Subnet-directed broadcasts are not considered secure and will leave a network open to potential denial of service (DoS) attacks. It is mostly disabled by default on routers and it is accepted as recommended best practice to leave it disabled.
Magic packets sent using subnet directed broadcast are forwarded by intervening routers, and then broadcast only once they reach the destination subnet. The computer with the specific MAC address in the magic packet will respond and wake up. For this method to be successful, all intervening routers must be configured to enable subnet-directed broadcasts forwarding.
Forwarding of subnet broadcasts leaves your network susceptible to denial of service attacks. Many wake-on-LAN solutions require the use of subnet directed broadcasts. However WakeUp is highly secure and scalable as it uses a dynamic agent discovery process to ensure that computers can be remotely and securely woken without the use of subnet directed broadcasts.
You can test if your network is capable of passing on directed subnet broadcasts by using the MagicTst.exe utility to send a single packet to a remote subnet and the RecvFrom.exe to test if magic packets are received by the target machine.
Integrating WakeUp with Configuration Manager
If you integrate WakeUp with Configuration Manager, the WakeUp server must be installed on all primary site servers with clients in the hierarchy. You must also install WakeUp onto the central site if you intend to wake computers directly from that computer's Configuration Manager administrator's console. WakeUp scans Configuration Manager for mandatory deployments. It uses system inventory information to send out wake-ups in time for the deployment schedule and contains extensions to the Configuration Manager Administrator console to explicitly wake-up single computers or whole collections.
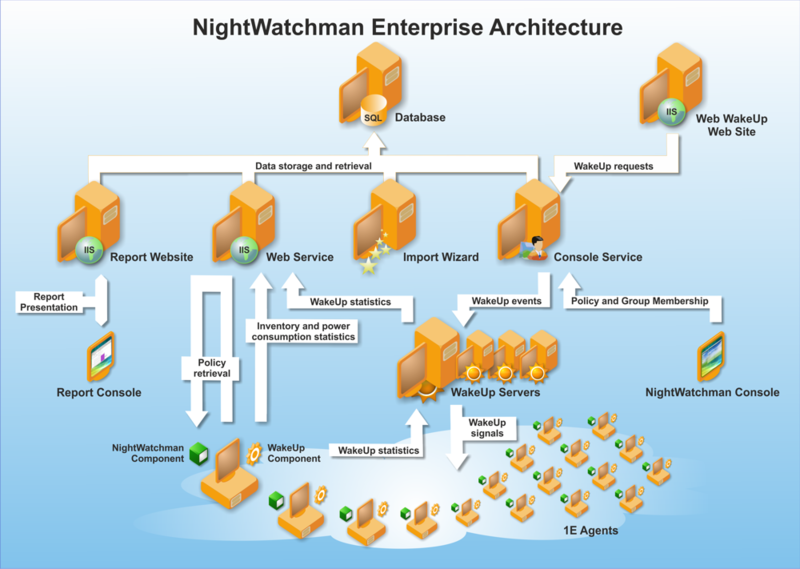
The WakeUp components are:
|
WakeUp component |
Explanation |
|---|---|
|
WakeUp server |
Responsible for calculating Configuration Manager deployments on a primary site server and for communicating with the 1E Agent. The WakeUp stores basic wake-up success statistics which can be viewed through the WakeUp console. WakeUp primary agents receive actions from the WakeUp server to send out magic packets to systems that need waking up. A local 1E Agent is installed on the WakeUp server as part of the WakeUp server installation. 1E Agents should be installed on all client end-points in order to be available to send out magic packets on their subnets. |
|
Configuration Manager administrator console extensions |
Enables administrators to selectively wake up computers or collections on-demand. |
-
The 1E Agent is a lightweight service which can be installed on a server or workstation.
-
WakeUp multi-agent mode is necessary if you want to use the extended reporting, policy refresh, automatic shutdown following a wake-up and the last man standing feature. It is also used if your network does not allow support for directed broadcasts and you do not want dedicated computers that are set to be on permanently.
-
The dedicated agent and stand-alone modes are now legacy and should only be used under direction from TeamViewer DEX Support.
-
The "WakeUp Agent" referred to in the following diagrams is the WakeUp module of the platform.
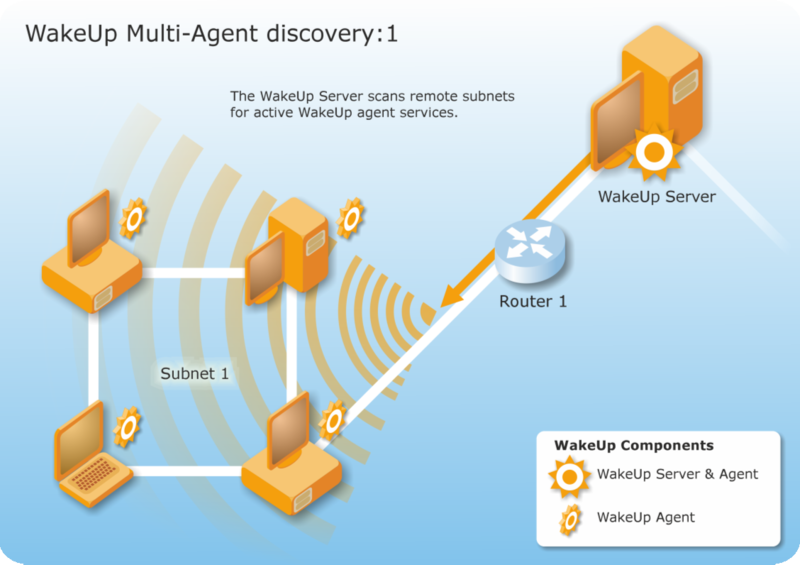
WakeUp Multi-Agent discovery process
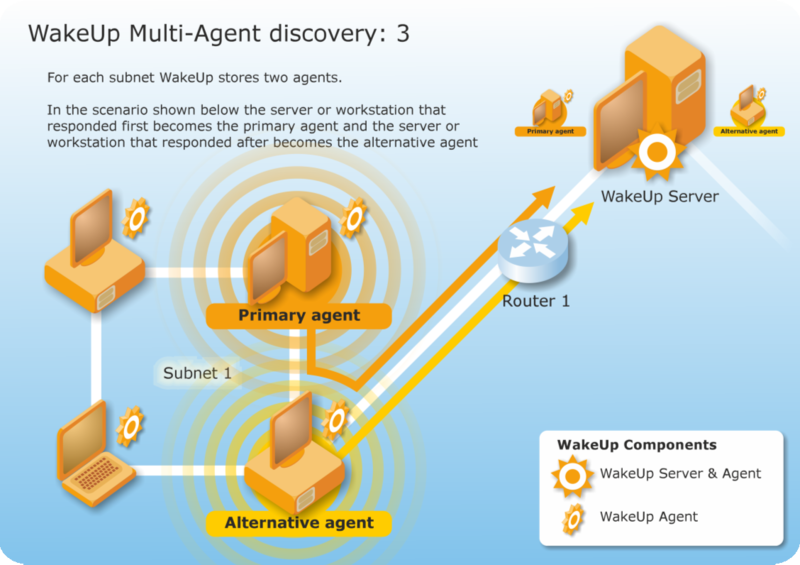
The WakeUp server communicates with the recently used primary agent. If this agent is unavailable, it attempts to use the previously discovered alternate agent. If neither are available, it attempts to locate other agents on that subnet.
-
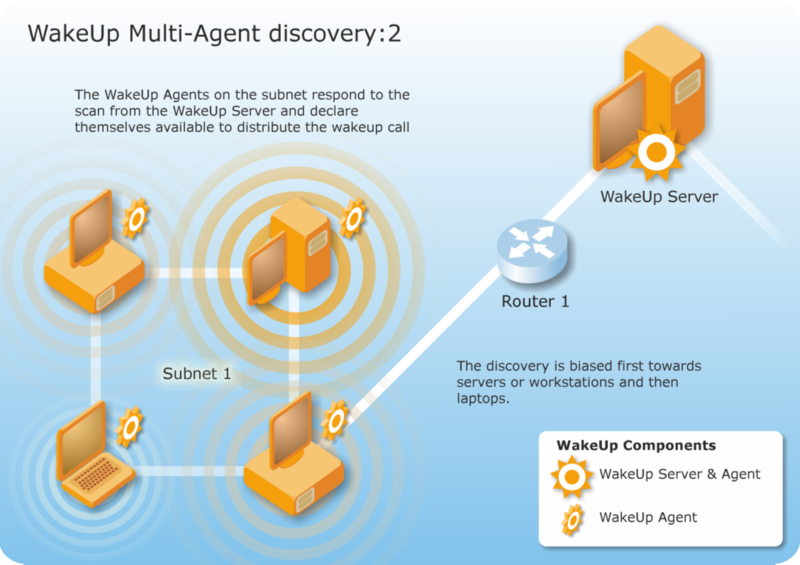
Target subnets are scanned by the WakeUp server for active agents. By default, the scan is biased towards servers or workstations on the subnet and lowest in the priority are laptops.
-
1E Agents respond to the WakeUp server by declaring themselves up and running and available to distribute wake up calls.
-
The first two agents to respond are stored by the WakeUp server on the Configuration Manager primary site server. The first agent is stored as the primary agent, the second becomes the alternate agent.
-
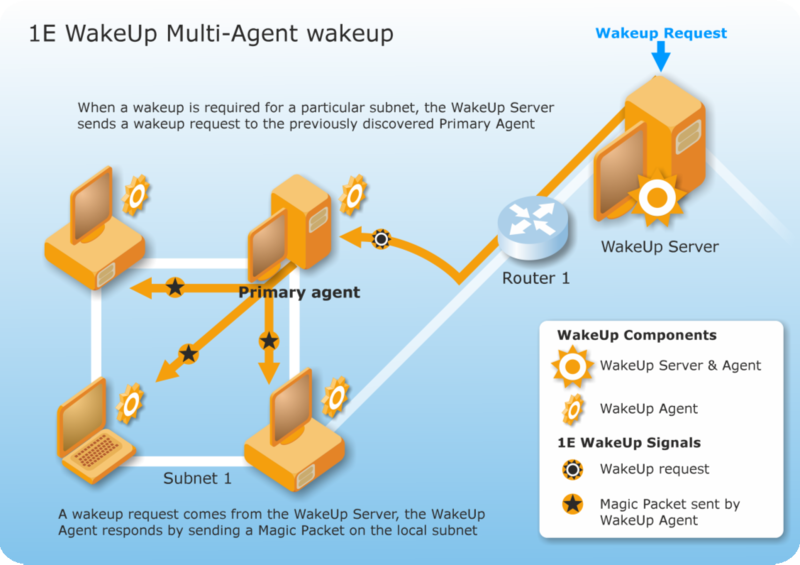
Once the primary agent has been established, the WakeUp server sends it a signal to wake up the targeted computers on its subnet, if it's with:
-
Configuration Manager - the wake-up request is prompted by a deployment or from the right-click context menu in the Configuration Manager Admin console
-
NightWatchman Management Centre - the wake-up request is prompted by an on-demand wake-up from the console or by an alarm clock or maintenance window for a specific machine.
-
Policy refresh
If you integrate with Configuration Manager and use the multi-agent mode, policy refresh is available to you. Systems that have just been woken up will immediately check Configuration Manager for new deployments. This significantly reduces the time taken for patch implementation, allowing more patches to take place in a given time period – particularly useful when you patch large number of systems overnight. Computers which are already on will check for a policy update immediately bypassing the normal polling cycle. Policy refresh works by sending a wake up to the computer that needs to be refreshed and can be tailored to your environment by using configuration options in the WakeUp Administrator console.
For example, in a minimal lab environment with one Configuration Manager server, one client and a five-minute polling interval, the lag time between a wake up and initiating a deployment for a computer which is already on can be reduced from seven to two minutes – a saving of over 60%. For longer polling periods, the time saved is even more significant.
Last man standing
WakeUp requires at least one computer is on per subnet. For the dedicated agent mode, you must ensure that the computer the agent is running on is always left on. In the multi-agent mode, you need to ensure that at least one of the computers in the subnet is left on. To make this easier, WakeUp provides Last Man Standing feature where the primary and alternate agents communicate with each other to prevent both of them being off at the same time.
If either of the primary or alternate agents gets turned off, they signal the other Agent. The other agent then knows that it is potentially in a Last Man Standing situation. If an attempt is made to shut it down, it sends a signal to its counterpart to wake up. This ensures that at least one of the agents is on, thereby providing constant coverage.
There are some edge cases where this may fail. For example, if a primary agent was hard powered-off, i.e. the power cable is unplugged, it will not have time to signal the alternate agent to wake up. If another computer is on, it will be found during the next agent discovery process and it will become the primary agent. However, if no other computer is available on that subnet, then neither a primary nor an alternate agent will exist and it will not be possible to wake up any computers until the next working day.
To prevent interfering with the last man standing feature, NightWatchman modifies its own behavior on WakeUp primary agent computers by:
-
Canceling requests for standby or hibernate
-
Converting shutdowns to re-boots (as long as NightWatchman logoffaction=Active)
-
The primary agent remains awake following a maintenance window.
How WakeUp works together with NightWatchman and Configuration Manager
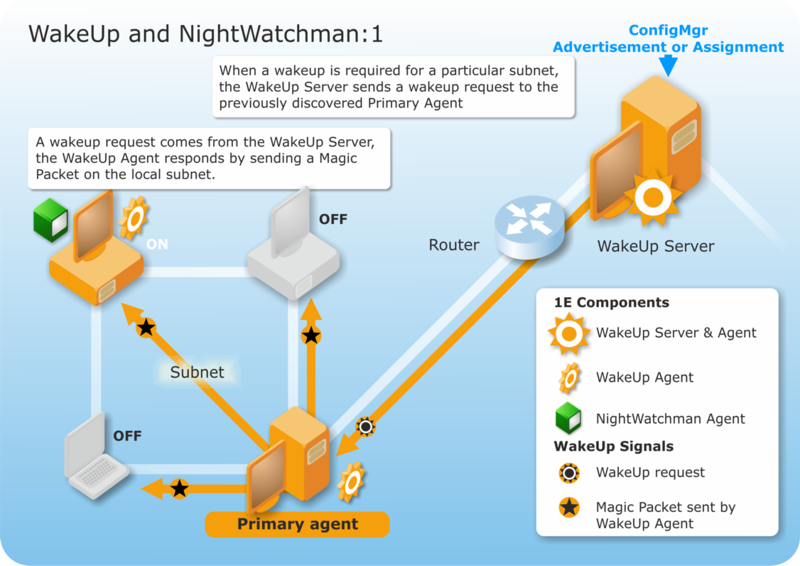
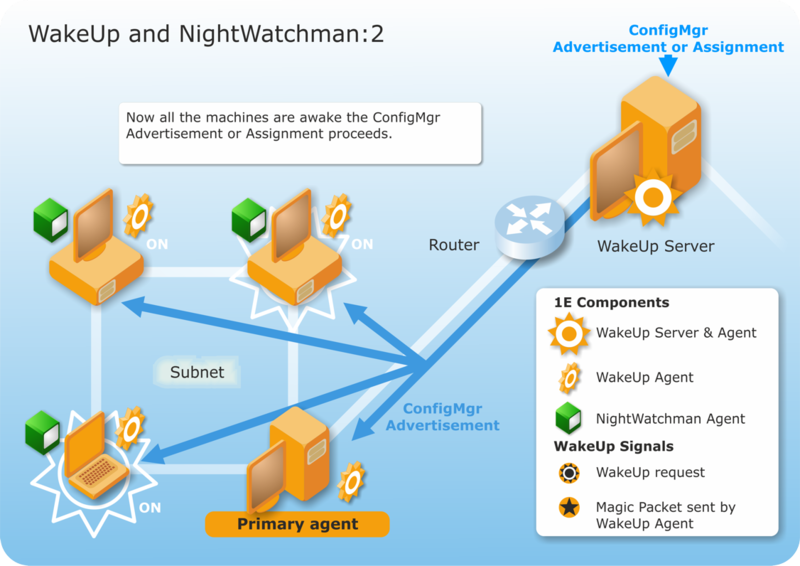
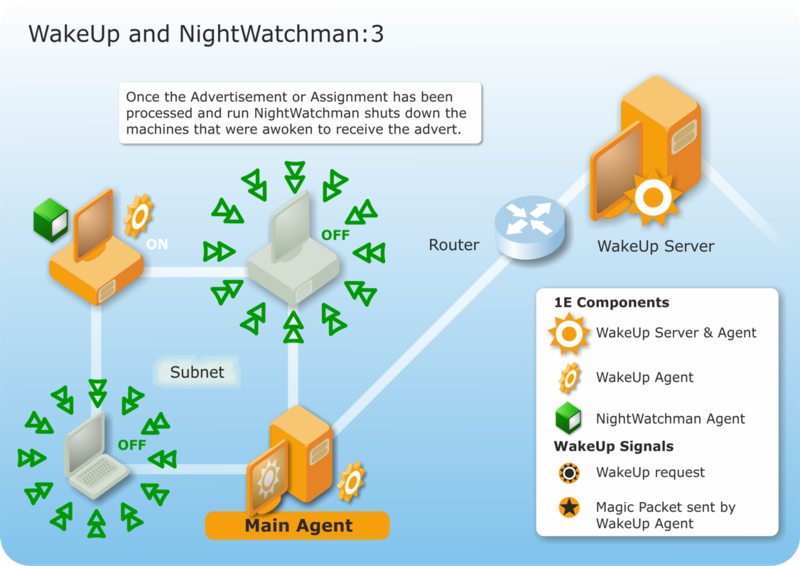
WakeUp and NightWatchman combine with Configuration Manager to provide a complete solution for scheduled software distribution. WakeUp can be used with Configuration Manager to ensure that computers are powered-on to receive a scheduled software distribution from Configuration Manager. NightWatchman ensures that all the awoken computers are powered-down after the software distribution to ensure minimum power usage.
For example, here's an illustration of how NightWatchman is configured to perform scheduled events and manage users who are logged on when the event starts. You may need to create additional scripts to add to the default set (Refer to Windows 1E NightWatchman Agent scripting reference and Mac 1E Agent scripting reference) that comes as part of a NightWatchman installation.
We are going to send a deployment or assignment to install new software during the night. On the left, are computers on a subnet with both WakeUp and NightWatchman installed. Two of the computers are powered-off and two are on. The main WakeUp agent wakes-up the powered-off computers by sending a magic packet.
The newly awoken computers are now in a position to receive the Configuration Manager deployment. If the deployment requires a reboot to complete the installation, NightWatchman saves open documents before the reboot.
On completion of the deployment, NightWatchman only shuts down the computers it wakes – energy savings are maximzed while still enabling the network to be easily patched, upgraded or distributed to.
Security
Encrypting WakeUp communications prevents packet sniffers from examining the contents of the packets sent between the WakeUp server and the agent and closes a potential security flaw where the packets could be examined to determine information about your network.
If you choose full encryption when you install WakeUp, any unencrypted communications are ignored. This prevents the new installation from working in conjunction with an earlier version where encryption was not supported. Installing WakeUp using partial encryption enables the use of both encrypted and unencrypted packets.
If you are upgrading and decide to make use of the encryption feature, you will either need to roll out the change simultaneously to every computer where WakeUp is installed or install it using partial encryption and upgrade all the WakeUp installations incrementally. The encryption feature can be introduced during the upgrade using the installer or from a command-line. Since the WakeUp 7.2.500 and later agent is a module of 1E Platform, see the 1E Client installation documentation for details.
The NightWatchman Management Center and its associated components can be configured to use FIPS. This is achieved with the USEFIPS installer property which must be set to the same value on the NightWatchman Management Center, WakeUp server and NightWatchman Agent.
How Web WakeUp works
Web WakeUp enables specific computers to be woken up from a website. It is primarily aimed at the user who needs to access their work computer from a remote location. Web WakeUp integrates with NightWatchman Enterprise to provide computer search and status capabilities. This means that the computers can be turned off when not in use with NightWatchman, thereby saving power, and can be woken up whenever they are needed by the user wherever they are. Web WakeUp has an API that enables its wake up functionality to be used by 3rd party applications. Web WakeUp has the following features:
|
Web WakeUp feature |
Explanation |
|---|---|
|
Increased scalability and performance |
It utilizes multiple WakeUp servers to allow scalable wake ups in your network. |
|
Multiple registered computers |
Up to twenty computers can be registered to be woken up by a single click from the Web WakeUp website. Refer to Web WakeUp. |
|
Website control |
Administrators can configure Web WakeUp pages that users see. Refer to Web WakeUp server configuration. |
|
Corporate branding |
You can customise the look and feel of the Web WakeUp website and integrate a Web WakeUp portal. Rrefer to Re-branding Web WakeUp and Integrating the Web WakeUp portal. |
|
Web WakeUp for iPhone and iPad |
Available as an iOS app that can be downloaded from the Apple App store. |
|
Support for mobile devices |
Web WakeUp lets you wake computers from your Blackberry or iPhone. Refer to Configuring Web WakeUp mobile devices. |
|
Remote desktop link |
You can RDP to your computer after a successful wake up. Refer to Configuring RDP settings. |
|
Locked-down security |
Register users who can wake up computers. Without the appropriate authorization they cannot search or wake up systems. |
|
Enhanced computer search |
Search for computers using domain\username combinations thereby increasing the compatibility between Web WakeUp and your networks. |
|
Increased accuracy |
Resolves local computer names without relying on DNS. It does this with an ActiveX control added to the client browser on first access. |
|
Extended API |
Wake up to 10,000 computers in a single call. The security and search functionality are in the Web WakeUp API. |
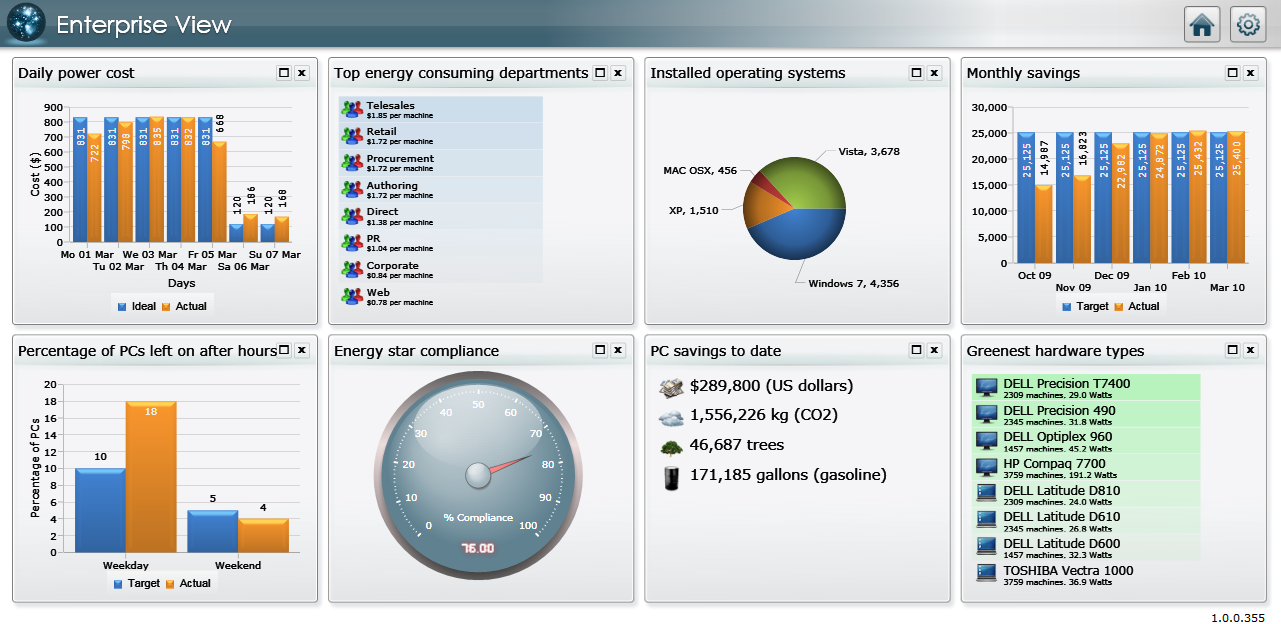
How Enterprise View works
Enterprise View is a web-based business intelligence dashboard that provides overviews of energy consumption and computer-related information from your network. You can customize the dashboard by choosing which tiles to display from a pre-defined list. It uses information already held in the reporting database to populate the tiles.