Single Site Download
The product formerly referred to as Nomad has been rebranded as Content Distribution. Although the new name is implemented in the majority of documentation and user interfaces, references to Nomad may still appear in specific tools, scripts, or contexts.
Learn how Single Site Download (SSD) feature minimizes WAN traffic by ensuring content is downloaded only once per site. Discover how SSD leverages local subnet awareness and peer-to-peer sharing to boost software deployment efficiency across enterprise networks.
Introduction
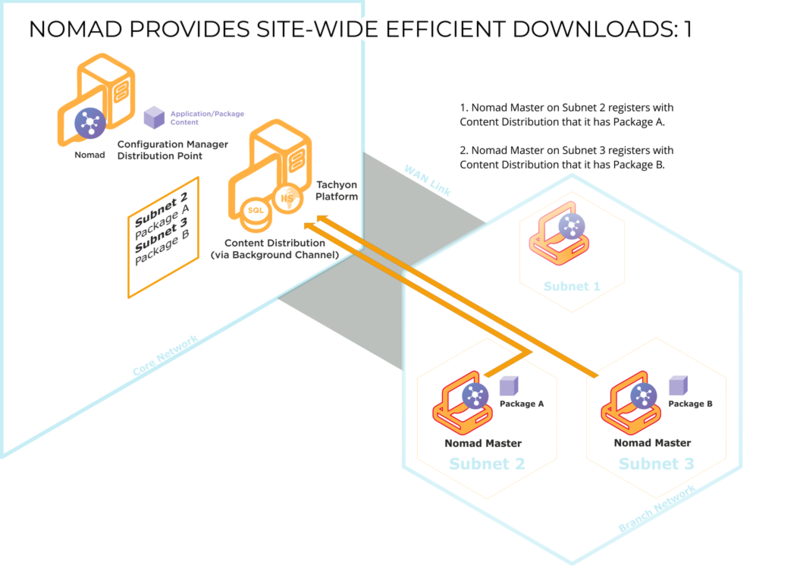
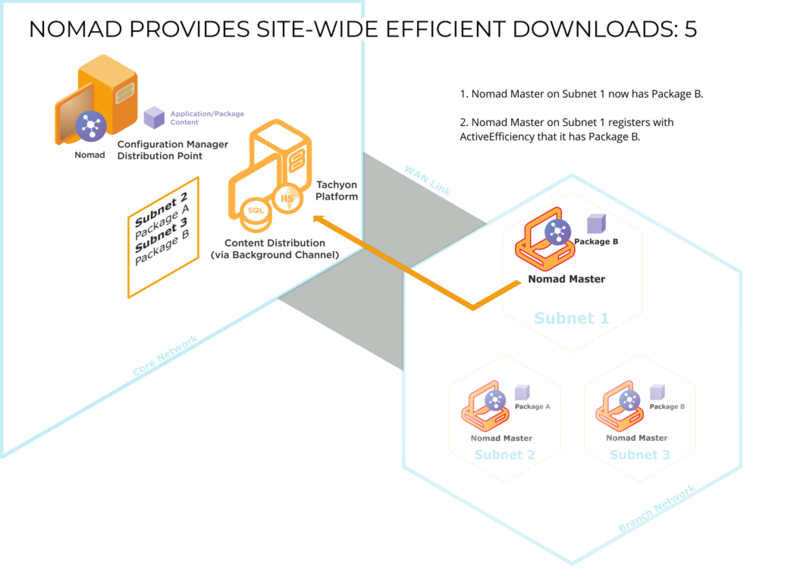
Single Site Download (SSD) ensures a download across the WAN only happens once per site. It does this by maintaining information about which subnets are neighbors of each other (accessible on LAN rather than WAN), so that when an elected master considers a download from a DP rather than a peer in its subnet, it can discover which other local subnets already have the package. These subnets are typically at a single customer site, specifically a single geographical location.
SSD uses Content Distribution. When a client downloads a package, it registers this information with Content Distribution, enabling a profile to be created on which Content Distribution clients hold particular packages.
Refer to Deploying software in large networks for scenarios for deploying software in large networks, utilizing Single-Site Download (SSD), and how you can monitor those deployments using the Content Distribution module.
Without SSD, an elected master for each subnet always accesses a Distribution Point (DP), often over a slow or congested WAN, even if a neighboring subnet in the LAN had the requested package. In practice, this had no major impact on WAN traffic as Content Distribution only uses a proportion of the current free network capacity rather than the total rated capacity, but efficiency can be improved by enabling access to Content Distribution caches on other subnets.
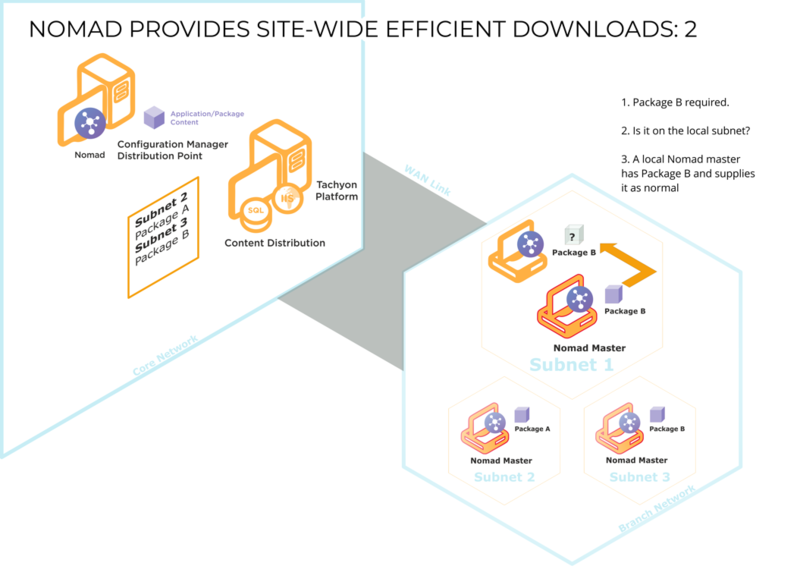
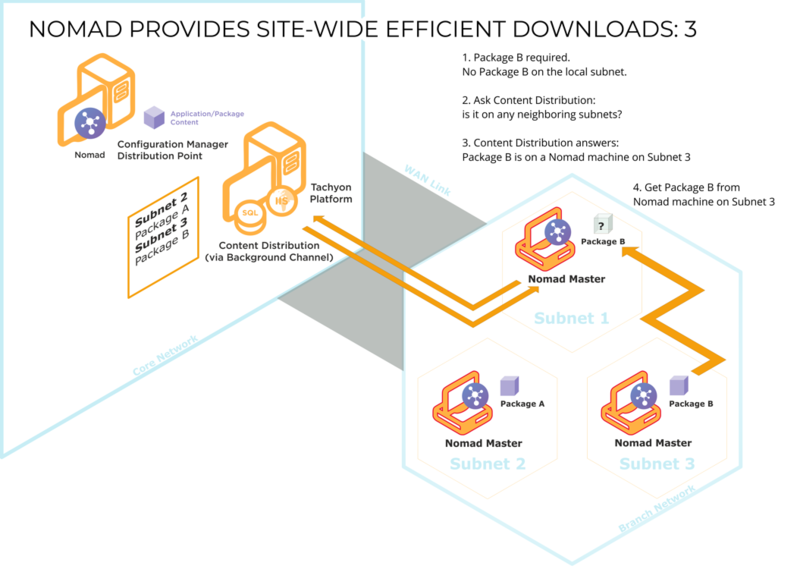
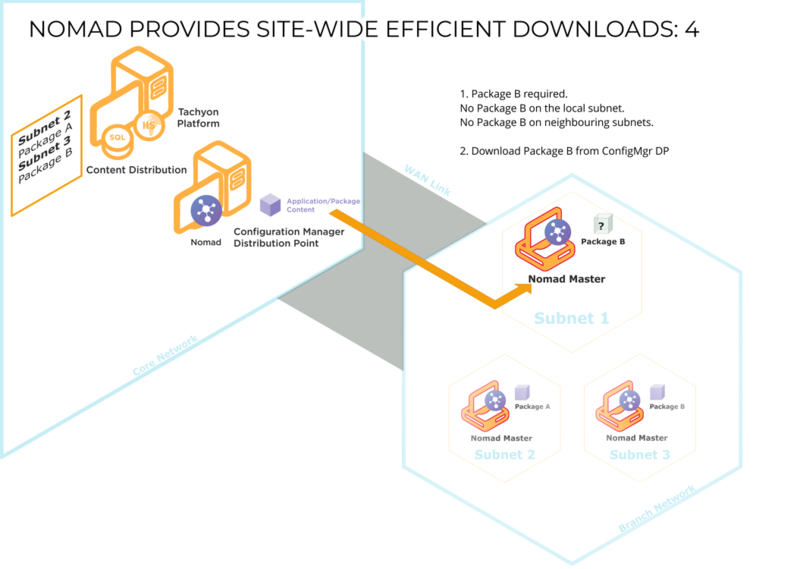
When a client requires a particular package, it attempts to find a copy on the local subnet. If it is unable to find one, it queries Content Distribution to see if there are clients on adjacent subnets that hold a copy. If it finds one, it will download the package from it; if it doesn't, it will download the package from the DP over the WAN as a last resort.
Content Distribution reacts dynamically to network adapter changes, and if its IP address changes it will automatically update its subnet information in Content Distribution. So, for example, closing the lid of a laptop and moving it to another subnet and resuming work there is handled by Content Distribution.
The following is how SSD interacts with other Content Distribution features:
-
SSD works seamlessly with Content Distribution FanOut . FanOut applies to peers and SSD applies to subnet masters.
-
SSD will use IP addresses if P2PEnabled registry value is set to use net literal names.
-
Work rates only apply to downloads from a DP not to P2P transfers, therefore they do not affect downloads from peers when using SSD.
-
When packages are purged from the cache, the corresponding entries are deleted from Content Distribution. Refer to Cache management. If you delete content directly from the cache, Content Distribution will not be aware that it has been removed and the corresponding Content Distribution record will not be deleted. If that host subsequently becomes a site master, it will inform requesting clients that it does not have the package, forcing them to request the package from the next master in the list.
The following restrictions apply:
-
The mechanism does not support Alternate source copy downloads, such as downloading an older version of a package from a LAN neighbor then filling in the changes.
-
Only the initial 0% downloaded of a package and the final percentage (which can be < 100% if the entire package cannot be downloaded) are registered with Content Distribution. There are no "10% so far" etc. intermediate records.
-
Even if a computer has multiple NICs, only details of one NIC and its subnet are used for SSD. If that NIC is unavailable, SSD will not work properly (although Content Distribution itself may be working correctly, using the DP rather than another site).
-
Remote differential compression (RDC) integration is not supported over SSD, it will not be used when a subnet master is copying from a site master.
-
IPv6 is not supported.
Refer to Enabling SSD in WinPE to make use of Content Distribution SSD in OS Deployment.
The local SSD feature was introduced to supplement site SSD for clients on networks such as wireless where broadcasts are disabled, to prevent each client becoming its own master and downloading direct from the DP. In a SSD enabled environment, a master queries Content Distribution to get a list of devices on other subnets within the site that have content. With local SSD enabled, the master also queries for devices having content within local subnet. If any local peers with content are available, then the master downloads from them, otherwise it attempts to download from Site peers (other subnets in the site), and if the master still cannot find any peers, it downloads the content direct from the DP.
In version 7.0 and later, a master skips using local SSD if it sees broadcast messages from peers. This means clients in mixed network environments can be configured with the same SSDEnabled setting (with Local SSD enabled) and clients can move seamlessly between networks. When on a wireless network (where broadcasts are typically disabled) local SSD can be used. On LAN networks (where broadcasts are typically allowed) local SSD would be skipped because a master is elected and sees broadcast activity from peers.
For details, refer to Nomad SSD architecture and ports
-
The information about sites and their associated subnets are stored and maintained in Content Distribution. When a client downloads a package, it registers this information with Content Distribution, enabling it to build a profile of which client holds particular packages and on which subnet.
-
When a client on a subnet requires a particular package, it first tries to find a copy on the local subnet using the standard method for retrieving cached The Content Registration Sync Cycle is available in Content Distribution 7.0 or later (1E Client 4.1 or later) which registers pending and failed content registrations with Content Distribution files.
-
If no local copy of the package is found it then tries Content Distribution database to see if any clients on other subnets at the same site hold a copy.
-
Only when all other avenues have failed will Content Distribution resort to downloading the package from the DP over the WAN.
-
When the master has a portion of the package it, registers itself with Content Distribution to say that it can provide this package to other subnets if required.
Fetching content
When Content Distribution receives a request to download content, an election takes place for a master. The master queries Content Distribution about neighboring subnets (accessible on LAN rather than WAN) so that it can download content from a peer in an adjacent subnet (within the same location) if that content is not available on a peer in its own local subnet. For each subnet, the top 10 clients (in terms of percentage cached by the client) are listed – the subnet containing the master is excluded from the list if no peer has the content. During this process, the percentage specified by the requesting client is ignored. Although neighboring clients may have a lower percentage than the requesting client, they may in fact have gained more since they last communicated with Content Distribution, so they are potentially useful sources for the package, hence the top 10 rule.
The master (now a subnet master) iterates through the list (which is sorted by percentage) and sends a package status request to each client. If it receives a response, the master attempts an SMB peer-to-peer download from that client (the current site master). If the attempt fails (it is not contactable or the limit on the number of concurrent connections is exceeded), it tries the next one in the list. If it fails to get the package from any of them, it downloads from the DP. If the list is empty, the master downloads from the DP. Clients with a lower percentage of the package than the client requesting it will not respond.
Content Distribution peers never deal with SSD; they only copy packages from their subnet's master. The subnet master may have the package completely cached or it may be actively downloading from another site or from a DP – the source makes no difference to the peer.
If a download is interrupted part way through (i.e. the source becomes unavailable), Content Distribution iterates through the remainder of the list and if it fails to get the package from any of them, it downloads from the DP.
When a download starts, Content Distribution registers the progress (0% of the content has been downloaded), and when it finishes, the final percentage is also recorded. As long as the content downloaded is greater than 0%, the host becomes a candidate for another client until the package is deleted from its cache. Records with status of 0% downloaded are purged from Content Distribution.
All clients that have SSD enabled will register content download with Content Distribution, not just the subnet master.
If the client is running as a guest on VMware, it registers itself as DeviceType=0 in the Content Distribution Consumer. Content Distribution excludes these devices from SSD query results as they are deemed ineligible to provide content.
Before enabling clients to use SSD, you need to ensure the following:
-
1E Platform is installed and running successfully.
-
The Content Distribution database is populated with information about sites and their associated subnets.
High-level overview of how to enable SSD
The following information applies to both new and existing installations of Content Distribution:
-
Make sure that 1E Platform is installed in your environment and is used as a content location metadata repository.
-
Within Content Distribution, populate the SSD sites and subnet information. A sample PowerShell script called PostADSitesandSubnets.ps1 is included in the Content Distribution installation files, which reads sites and subnets from AD.
-
Content Distribution captures a list of background channels from the 1E Client in the BackgroundChannelUrl and uses the first working URL as the PlatformURL by appending /Proxy/ContentDistribution/ if this PlatformURL is unreachable it attempts to connect to the next BackgroundChannelUrl.
-
Enable SSD on all Content Distribution agents, by modifying HKLM\Software\1E\NomadBranch\SSDEnabled to 3, this enables SSD for both "Provide" and "Consume" modes, specifically Content Distribution will provide content to other peers and consume content from other peers.
-
If you already have Content Distribution installed and are only now enabling SSD, then ensure HKLM\Software\1E\NomadBranch\Platform\ContentRegistration is set to 1, in other words Content Distribution will register downloaded content, this is automatically enabled for new installations, and SSD.
If you have clients on networks where broadcasts are disabled (for example wireless) then enable local SSD by setting SSDEnabled=7. Also set ContentProviderOnWifi=1.
IPv6 Protocol-Aware Filtering
For Content Distribution and PXE Everywhere:
To minimize WAN bandwidth usage, the client requests a list of peer devices from Content Distribution that already possess the required content or version. This list may include devices with either IPv4 or IPv6 addresses. However, the requesting (source) device might not be able to communicate with some of the returned devices due to protocol stack incompatibilities (e.g. IPv4-only device trying to reach an IPv6-only device).
To address this, two configuration flags are used:
-
IPv4IPv6CommunicationSupported: At the subnet level.
-
IPv4IPv6CommunicationEnabledForAllSubnets: At the global level.
These flags determine whether devices that support both IPv4 and IPv6 communication should be included in the returned list. By filtering based on protocol compatibility, the system reduces failed connection attempts and improves overall performance.
Building a subnet profile in Content Distribution
To build a subnet profile for SSD and the peer backup assistant feature, Content Distribution must communicate with its web service. When theContent Distribution service starts, it connects and registers the hosting device by name with Content Distribution, which returns a device ID in the form of a GUID that enables it to uniquely identify the client and its default subnet. If it is unable to communicate with Content Distribution, it retries every 5 minutes until it succeeds (as long as SSD is enabled). An attempt to communicate with Content Distribution is also made prior to a package download to register its status. Refer to Enabling SSD in WinPE
Note the following:
-
On a multi-NIC host, only one NIC gets registered, and a wired interface takes precedence over a wireless interface during registration.
-
If Content Distribution fails initially to register an adapter, it retries every 5 minutes (for as long as SSD is enabled) until it succeeds.
-
Wireless adapters can be configured to act as SSD content providers and consumers. Use the ContentProviderOnWifi registry setting to do this.
-
If the initial device registration was successful when the Content Distribution service started, but Content Distribution later becomes unavailable, when Content Distribution subsequently downloads and caches a package it will not be able to register the package (see below for details). Content Distribution does not re-attempt package registration, so it will not know that this particular Content Distribution host has the package.
Example PowerShell scripts
You can get information about sites and subnets from AD, or by other means. Example PowerShell scripts can be used for retrieving information about sites and their associated subnets from the AD and updating the Content Distribution database. Refer to Content Distribution Tools.
Viewing Nomad sites and subnets in the Content Distribution app
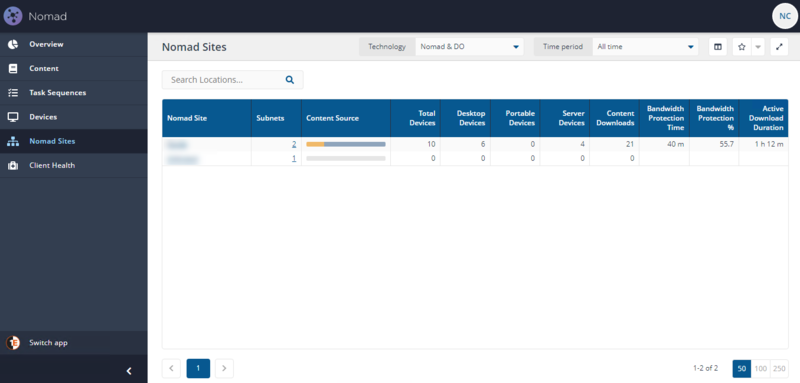
The sites and subnets stored in Content Distribution are visible in the Nomad Sites page of the Content Distribution app.
-
The Nomad Sites page is primarily designed to show how the network is being used for content distribution in different locations. It focuses on the volume of content downloaded from peers vs over the WAN, rather than the status of specific content titles in a given site. You can see what content is available in a given site by looking at the Content tab for that site.
-
A Nomad Site corresponds to Nomad Single Site Download (SSD) site. Customers that have implemented SSD and upgrade ActiveEfficiency to the Content Distribution app will see their defined SSD locations displayed as Nomad Sites.
-
Any subnets that are not included in a Content Distribution SSD Site definition will be represented in a site named Unknown. If no SSD sites have been defined, all subnets will be included in the Unknown site.
The app provides visibility of activity and cache status for content distributed by both Content Distribution and Delivery Optimization. This includes Configuration Manager content distributed with Content Distribution and Software Updates content distributed with either Content Distribution or Delivery Optimization.
Uninstallation, reinstallation and reactivation
When you uninstall a client, all its registry values are deleted. However, if you subsequently reinstall it, the device ID returned when Content Distribution next registers is one that is recycled from the database – this is because that is the device registered for the named computer, so it recognizes that the same computer is involved and restores the previous values to the registry.
If you change the host name or domain, Content Distribution will regard this as a new computer and generate a new device ID for it.
If a cached package is reactivated, such as after an OSD upgrade or cloning, Content Distribution will register the package. (If this is a re-registration, the Content Distribution record is effectively unchanged).
Improved resilience of content registration
Registrations can fail when Content Distribution or the SQL Server hosting the ContentDistribution database is busy, overloaded or down for maintenance, resulting in content registration mismatch between the clients and Content Distribution.
The following registry setting is used by the Content Registration Sync Cycle feature.
|
Registry value |
Type |
Default |
Notes |
Installer property |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
REG_DWORD |
1440 (1day) |
Range: from 60 to 525600 (1Year). |
MODULE.NOMAD.CACHESTATESYNCINTERVALMINUTES |
To enable SSD in WinPE:
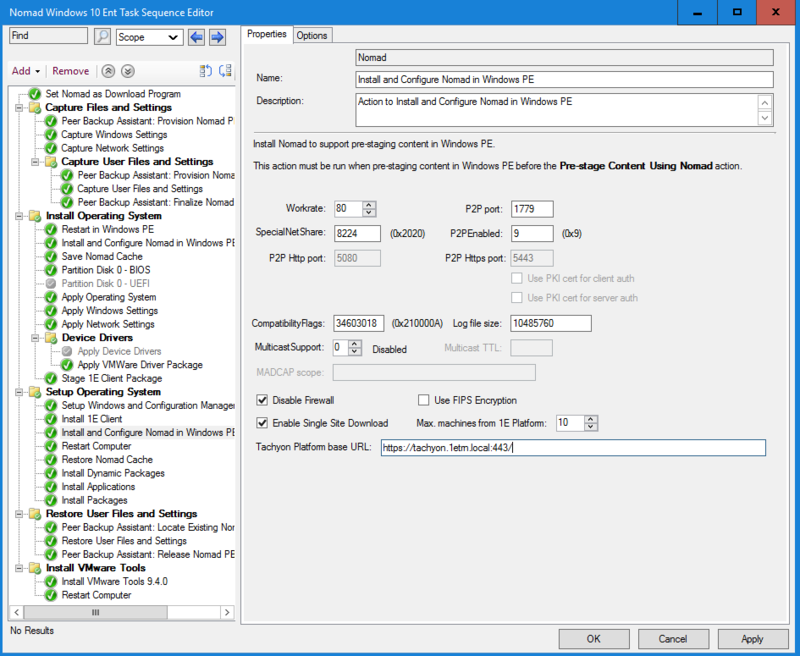
-
Edit the task sequence for which you want to use SSD.
-
Enable Single Site Download.
-
In 1E Platform base URL: enter for example, https://<server_FQDN:port/ or http://<server_FQDN:port/ depending on the protocol you are using, where <server_FQDN> is the FQDN of the 1E server or its DNS alias.
-
Click OK.
After upgrade you will need to update any pre-existing task sequences using this step to reflect the move from ActiveEfficiency to the Platform.